WebSocket 实现简易聊天室
消息推送的常见方式
1.轮询 浏览器以指定的时间间隔向服务器发出HTTP请求,服务器实时遮回数据给浏览器
2.长轮询 浏览器发出ajax请求,服务器端接收到请求后,会阻塞请求直到有数据或者超时才返回
3.SSE(server-sent event)服务器发送事件
SSE在服务器和客户端之间打开一个单向通道
服务端响应的不再是一次性的数据包,而是text/event-stream类型的数据流信息
服务器有数据变更时将数据流式传输到客户端
4.WebSocket Websocket是一种在基于TCP连接上进行全双工通信的协议
TIP
全双工: 全双工(Full Duplex):允许数据在两个方向上同时传输
半双工: 半双工(Half Duplex):允许数据在两个方向上传输,但是同一个时间段内只允许一个方向上传输。
客户端
客户端方法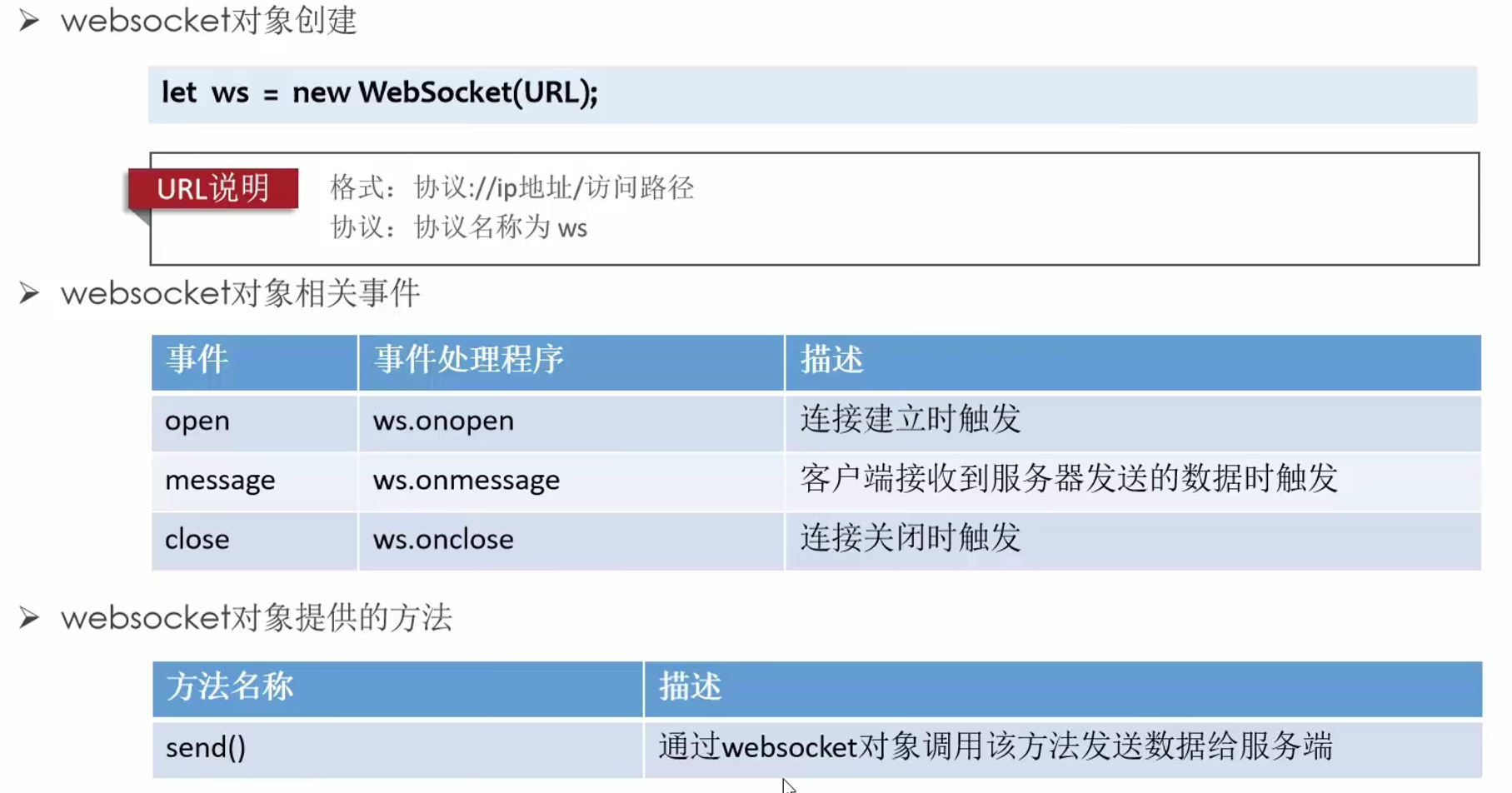
代码概览
服务端
Tomcat的7.0.5 版本开始支持WebSocket,并且实现了Java WebSocket规范。
Java Websocket应用由一系列的Endpoint组成。Endpoint 是一个java对象,代表Websocket链接的一端,对于服务端,我们可以视为处理具体WebSocket消息的接口。
如何定义Endpoint?
我们可以通过两种方式定义Endpoint:
第一种是编程式, 即继承类javax.websocket.Endpoint并实现其方法
第二种是注解式, 即定义一个POJO, 并添加@ServerEndpoint相关注解
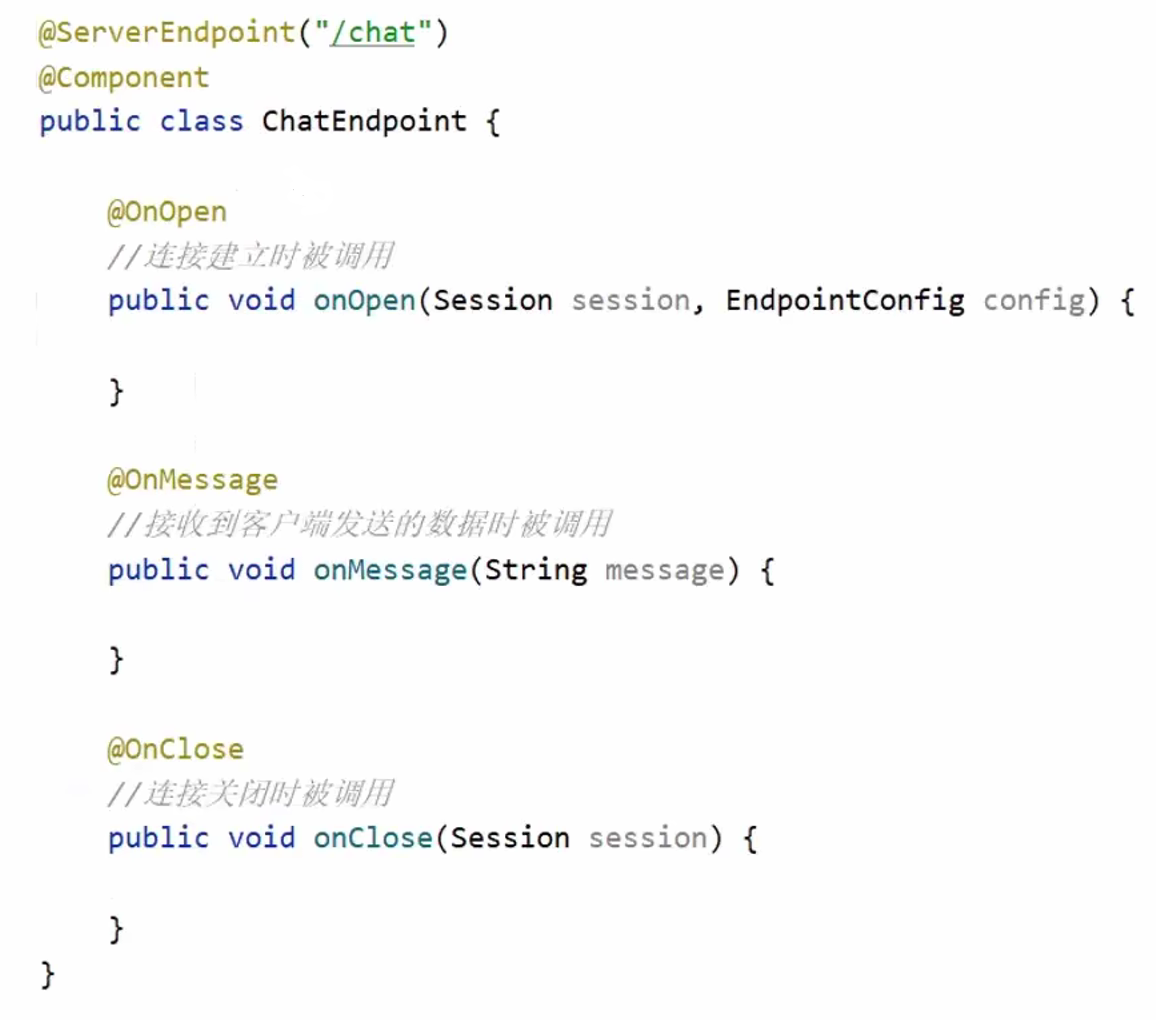
生命周期方法
Endpoint实例在Websocket握手时创建,并在客户端与服务端链接过程中有效,最后在链接关闭时结束。
在Endpoint接口中明确定义了与其生命周期相关的方法, 规范实现者确保生命周期的各个阶段调用实例的相关方法。
生命周期方法如下:

DANGER
⬆ 没有onError,应为onMessage @OnMessage
服务端如何接收客户端发送的数据?
1.编程式 通过添加 MessageHandler 消息处理器来接收消息
2.注解式 在定义Endpoint时,通过@OnMessage注解指定接收消息的方法
服务端如何推送数据给客户端?
发送消息则由 RemoteEndpoint 完成,其实例由Session 维护发送消息有2种方式发送消息
方式1:通过session.getBasicRemote 获取同步消息发送的实例,然后调用其 sendXxx()方法发送消息
方式2:通过session.getAsyncRemote 获取异步消息发送实例,然后调用其 sendXxx()方法发送消息
代码概览
SpringBoot整合Websocket
引入依赖
xml
<!--websocket-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
</dependency>配置类
编写配置类,扫描添加有@ServerEndpoint注解的Bean
该配置类会自动扫描带有@ServerEndpoint注解的
java
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig {
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}编写配置类,用于获取HttpSession对象
java
public class GetHttpSessionConfig extends ServerEndpointConfig.Configurator {
@Override
public void modifyHandshake(ServerEndpointConfig sec, HandshakeRequest request, HandshakeResponse response) {
// 获取HttpSession对象
HttpSession httpSession = (HttpSession) request.getHttpSession();
// 将httpSession对象保存起来
sec.getUserProperties().put(HttpSession.class.getName(), httpSession);
}
}定义Bean,在@serverEndpoint中引入配置器
java
@ServerEndpoint(value = "/chat", configurator = GetHttpSessionConfig.class)
@Component
public class ChatEndPoint {
private static final Map<String, Session> onlineUsers = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private HttpSession httpSession;
/**
* 建立websocket连接后,被调用
*
* @param session
*/
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session, EndpointConfig config) {
// 1.将session进行保存
this.httpSession = (HttpSession) config.getUserProperties().get(HttpSession.class.getName());
String userName = (String) this.httpSession.getAttribute("userName");
onlineUsers.put(userName, session);
// 2. 广播消息,需要将登录的所有用户推送给所有用户
String message = MessageUtil.getMessage(true, null, getAllUserName());
broadcastAllUsers(message);
}
/**
* 浏览器发送消息到服务端,该方法被调用
*
* @param message
*/
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message) {
// 将消息推送给指定用户
Message msgObj = JSON.parseObject(message, Message.class);
// 获取消息接收方
String toName = msgObj.getToName();
String msg = msgObj.getMessage();
// 接收方 session对象
Session session = onlineUsers.get(toName);
String sendMsg = MessageUtil.getMessage(false, (String) this.httpSession.getAttribute("userName"), msg);
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText(sendMsg);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 断开websocket连接时被调用
*
* @param session
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose(Session session) {
// 1.从onlineUsers中剔除当前用户的session对象
onlineUsers.remove((String) this.httpSession.getAttribute("userName"));
// 2.通知其他所有用户,当前用户下线了
String message = MessageUtil.getMessage(true, null, getAllUserName());
broadcastAllUsers(message);
}
private Set getAllUserName() {
Set<String> strings = onlineUsers.keySet();
return strings;
}
private void broadcastAllUsers(String message) {
onlineUsers.forEach((k, v) -> {
// 获取所有用户的session对象
Session session = v;
// 发送消息
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
}
}注意
在onOpen中的EndpointConfig 与 GetHttpSessionConfig类中modifyHandshake方法的ServerEndpointConfig这俩其实是一个对象
保存HttpSession对象时 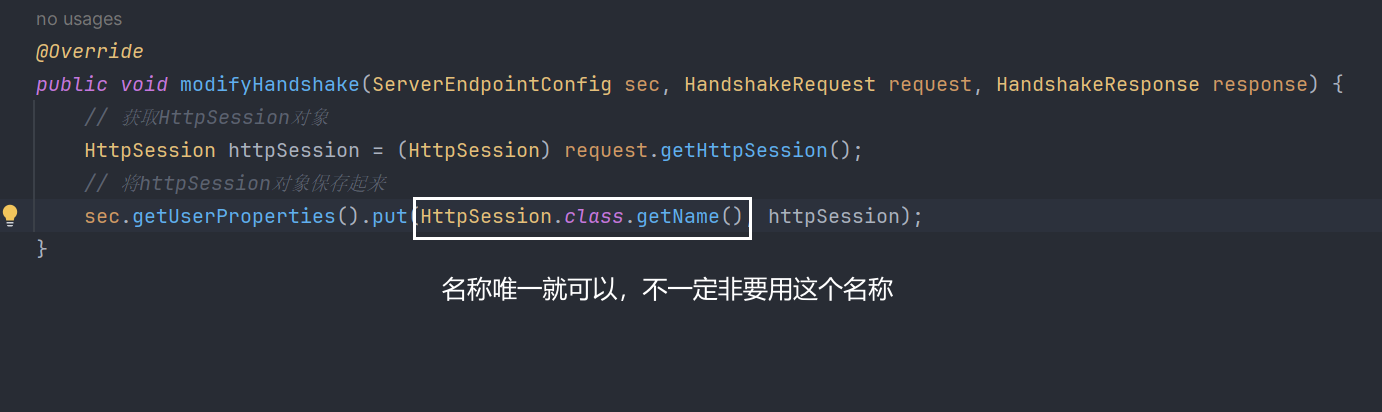
用到的代码片段
java
public class MessageUtil {
public static String getMessage(boolean isSystemMessage, String fromName, Object message) {
ResultMessage resultMessage = new ResultMessage();
resultMessage.setMessage(message);
resultMessage.setSystem(isSystemMessage);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(fromName)) {
resultMessage.setFromName(fromName);
}
return JSON.toJSONString(resultMessage);
}
}java
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class Message {
private String toName;
private String message;
}java
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class ResultMessage {
private boolean system;
private Object message;
private String fromName;
}消息格式

SSE(Server-Sent Events)
什么是 SSE
服务器发送事件(Server-Sent Events,简称SSE)
SSE,就是浏览器向服务器发送一个HTTP请求,然后服务器不断单向地向浏览器推送“信息”(message)。
这种信息在格式上很简单,就是“信息”加上前缀“data:”,然后以“\n\n”结尾。
SSE 应用场景
服务器向浏览器“发送”数据,比如,每当收到新的电子邮件,服务器就向浏览器发送一个“通知”
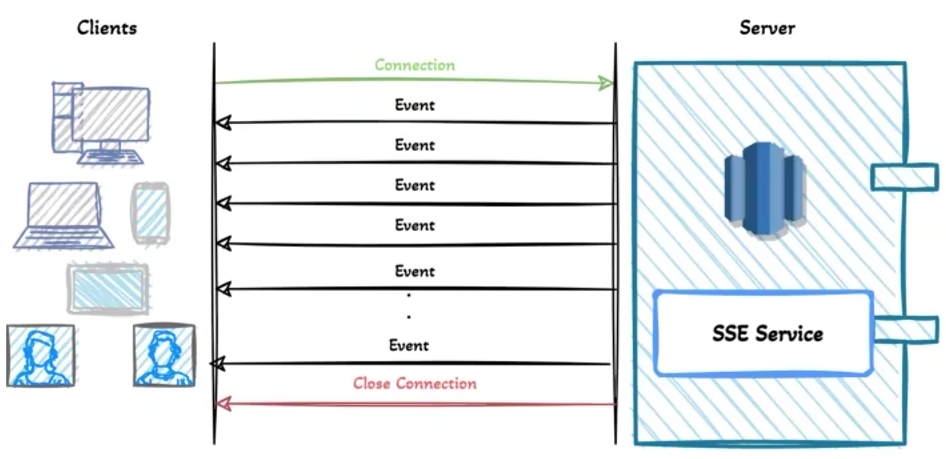
SSE 与 Websocket
SSE 与 WebSocket 有相似功能,都是用来建立浏览器与服务器之间的通信渠道。两者的区别在于:
- WebSocket 是全双工通道,可以双向通信,功能更强;SSE 是单向通道,只能服务器向浏览器端发送。
- SSE 是一个轻量级协议,相对简单; WebSocket 是一种较重的协议,相对复杂。
实现方式 1
前端
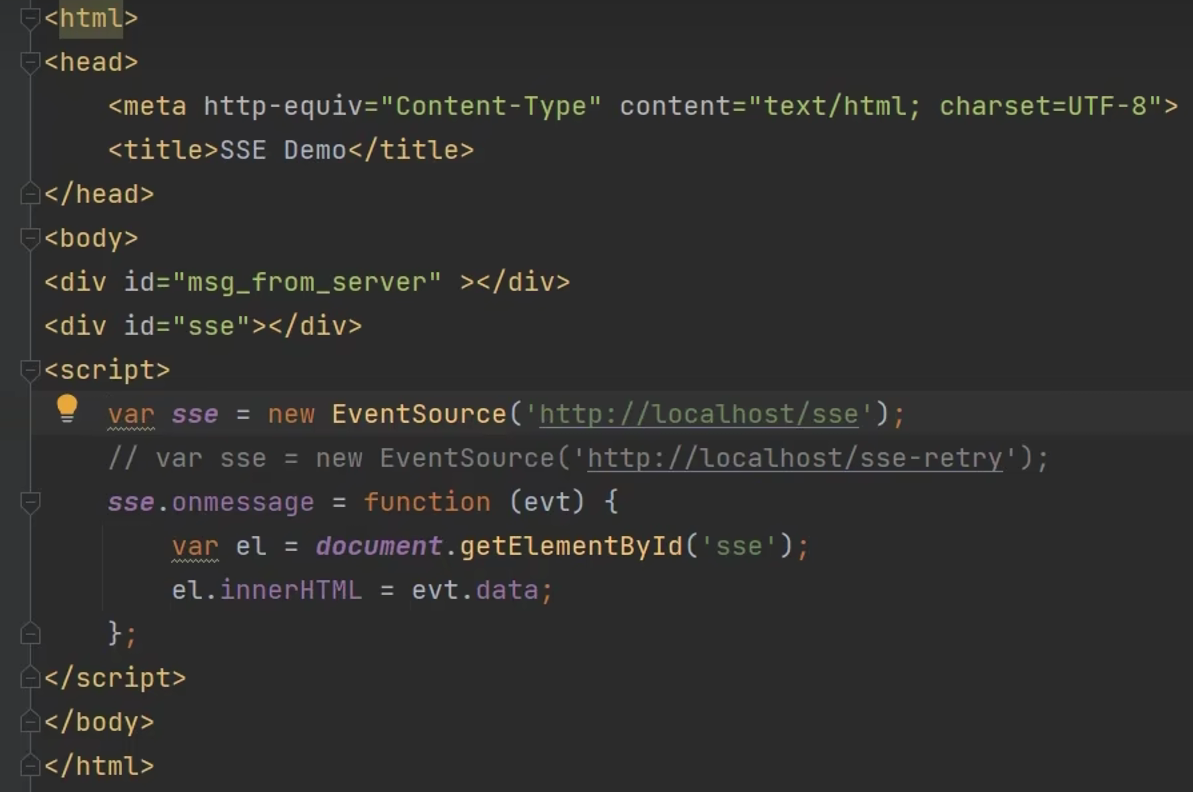
后端
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/messageObtain")
@Slf4j
public class MessageNoticeController {
@PostMapping("/getStreamData")
public String getStreamData(HttpServletResponse response) {
response.setContentType("text/event-stream");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String str = "";
while (true) {
str = "data:" + new Date() + "\n\n";
PrintWriter writer = null;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
writer = response.getWriter();
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
writer.write(str);
// log.info(str);
writer.flush();
}
}
}TIP
响应是主要的
response.setContentType("text/event-stream");
实现方式 2
前端
vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>SSE Messages</h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="message in messages" :key="message.id">{{ message.data }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { onMounted, ref } from 'vue';
interface SseMessage {
id: string;
data: string;
}
const messages = ref<SseMessage[]>([]);
onMounted(() => {
const eventSource = new EventSource('http://localhost:8080/api/sse/events');
eventSource.onmessage = (event) => {
const parsedData: SseMessage = JSON.parse(event.data);
messages.value = [...messages.value, parsedData];
};
eventSource.onerror = () => {
console.error('EventSource failed.');
eventSource.close();
};
});
</script>
<style scoped>
/* Add some styles here */
</style>后端
java
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.SseEmitter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/sse")
public class SseController {
private final ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
@GetMapping(value = "/events", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public SseEmitter handleSse() {
// 设置超时时间为1小时
SseEmitter emitter = new SseEmitter(3600000L);
// 处理客户端断开连接回调
emitter.onCompletion(() -> {
System.out.println("Connection completed");
});
// 设置超时回调
emitter.onTimeout(() -> {
System.out.println("Connection timed out");
emitter.complete();
});
// 设置错误回调
emitter.onError((ex) -> {
System.err.println("SSE 连接出错: " + ex.getMessage());
emitter.completeWithError(ex);
});
// 模拟每两秒发送一次消息到客户端,总共发送十次
executorService.execute(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
SseEmitter.SseEventBuilder event = SseEmitter.event()
.data("SSE message " + i)
.id("" + i)
.name("sseEvent");
emitter.send(event);
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
emitter.complete();
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
emitter.completeWithError(e);
}
});
return emitter;
}
}实现方式 3
java
package com.example.ssedemo.controller;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.SseEmitter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/sse")
public class SseController {
private final ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
@GetMapping(value = "/stream", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public SseEmitter streamEvents() {
// 创建一个 SseEmitter 实例,设置超时时间为 0(永不超时)
SseEmitter emitter = new SseEmitter(0L);
// 异步发送事件
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
// 模拟每秒发送一次数据
Thread.sleep(1000);
emitter.send(SseEmitter.event()
.id(String.valueOf(i))
.name("message")
.data("Event " + i));
}
// 完成事件流
emitter.complete();
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
emitter.completeWithError(e);
}
});
return emitter;
}
}vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>Server-Sent Events (SSE) Demo</h1>
<button @click="startSSE">Start SSE</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(event, index) in events" :key="index">{{ event }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue';
// 定义响应式变量
const events = ref<string[]>([]);
let eventSource: EventSource | null = null;
// 启动 SSE 连接
const startSSE = () => {
if (eventSource) {
eventSource.close(); // 如果已经有连接,先关闭
}
// 创建 EventSource 连接到后端 SSE 端点
eventSource = new EventSource('http://localhost:8080/sse/stream');
// 监听消息事件
eventSource.addEventListener('message', (event: MessageEvent) => {
console.log('Received event:', event.data);
events.value.push(event.data); // 将接收到的消息添加到列表中
});
// 监听错误事件
eventSource.onerror = (error: Event) => {
console.error('EventSource failed:', error);
eventSource?.close(); // 关闭连接
};
};
</script>
<style scoped>
ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
}
li {
margin: 5px 0;
}
</style>